Global commissioning of onshore wind turbines declined 3 percent in 2018, partly due to a slowdown in India and Germany. Growth is expected to bounce back in 2019, with a 32 percent jump to 60 GW.
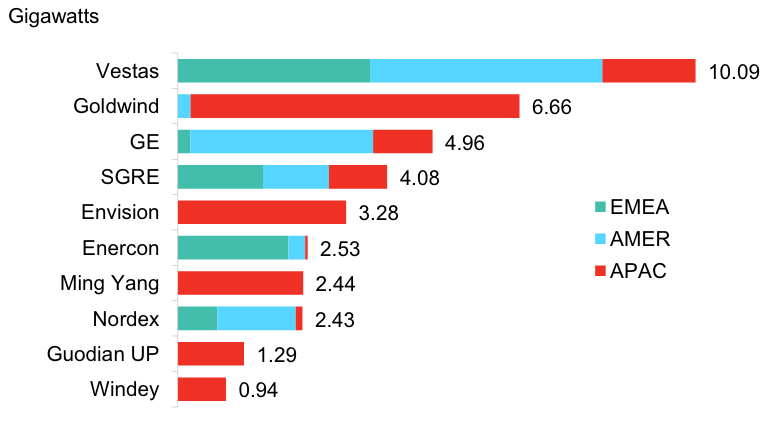
Developers commissioned a little over 45 GW of onshore wind turbines globally in 2018 compared with 47 GW a year earlier. Just four manufacturers accounted for more than half, or 57 percent, of the machines deployed: Denmark’s Vestas, China’s Goldwind, GE Renewable Energy of the U.S. and Spain’s Siemens Gamesa, according to the latest data from from BloombergNEF (BNEF).
Vestas extended its lead in the industry, with 10.1GW of its onshore turbines commissioned in 2018 – a global market share of 22 percent compared with 16 percent in 2017, said BNEF.
China’s Goldwind rose from third to second place, lifted by a strong performance in China, where it captured a third of the 19.3 GW market. The company’s global footprint, however, remains limited: only 5 percent of Goldwind’s 6.7 GW were commissioned outside China. GE came third with 5 GW – six out of every ten GE turbines were commissioned in the U.S. Both GE and Vestas commissioned just over 3 GW in the U.S., with Vestas leading by 44 MW in the neck-to-neck race for U.S. market leadership.
Siemens Gamesa, formed in 2016 from a merger of the wind business of German engineering giant Siemens and the Spanish turbine maker Gamesa, dropped from second to fourth place, with 4.1 GW commissioned in 2018. This is 40 percent less than in 2017, although the tally does not include a number of very large wind farms that are only partially built and will not come online until 2019.
“Chinese manufacturers rely almost solely on their home market,” said Tom Harries, senior wind analyst at BNEF and lead author of the BNEF report Global Wind Turbine Market Shares. “Of the European onshore wind turbine makers to make the top 10, Vestas and Nordex actually commissioned more capacity in the Americas than in Europe. Most of Enercon’s turbines are in Europe. Siemens Gamesa is the most diversified, with a near equal split across Europe, the Americas and Asia.”
“In offshore wind, it’s been a record year for China, and we will see more growth,” Harries continued. “Some 1.7 GW of the global 4.3 GW was commissioned there. In Europe it was a tight race between Siemens Gamesa and MHI Vestas. GE has some projects coming up in France, and we also expect to see orders for their new 12MW platform.”
Total onshore wind installations in 2018 were 11.7 GW in the Americas, 8.5 GW in Europe (including Turkey and Russia) and 1 GW in Africa and the Middle East, while Asia accounted for 24.2 GW.
BNEF registered new wind farms starting full commercial operation in 53 countries.
David Hostert, head of wind research at BNEF, said: “Now it is time for the manufacturers to buckle up for two stormy years ahead: we predict demand for around 60 GW of onshore capacity in both 2019 and 2020 with increases in all regions. However, a lot of this impressive-sounding volume rides on extremely competitive pricing, add-on products and services, and new financing models. This will be tough to deliver for the Big Four, let alone the smaller turbine makers.”
Trends in wind turbines are discussed at POWERGEN International and we’re accepting abstracts until February 19. Submit yours today.